(SEP 2022) Dr. Richard Tai Chiu HSUNG has research collaboration with Dr Walter Lam, Clinical Assistant Professor in the Faculty of Dentistry, the University of Hong Kong and Prof. Wai Lun LO, Professor and Head CS dept. Dr. Richard Tai Chiu HSUNG, Associate Professor, CS dept. has successfully got research funding for the following project. It is expected that the project will start in Jan 2022.
Automatic multiple level gum disease detection based on deep neural network: algorithm and system
Dr. Richard Tai Chiu HSUNG (PI) Associate Professor, CS dept., CHCHE
Dr Walter Lam (Co-I) Clinical Assistant Professor in the Faculty of Dentistry, Member of the HKU Musketeers Foundation Institute of Data Science, The University of Hong Kong
Prof. Wai Lun LO (Co-I) Head of CS dept., Associate Dean FSE, CHCHE
Research Grant Committee, Hong Kong, Faculty Development Scheme (FDS), 36 months, HK$ 1,181,781, UGC/FDS13/E01/22
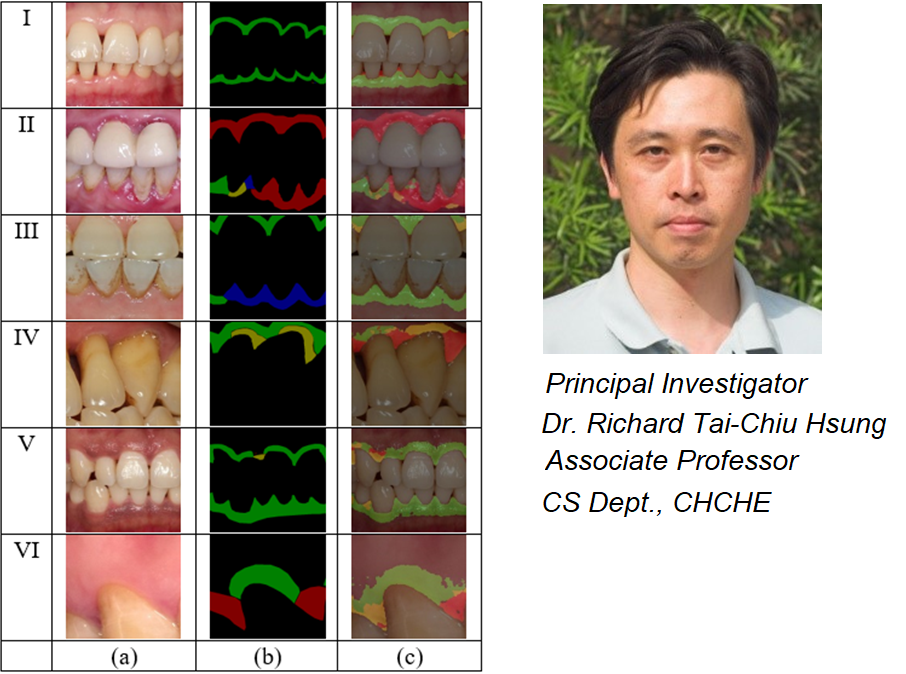
Fig 1. Selected prediction results on the validation dataset using the proposed AI system. Rows (I)-(VI) show the input images and prediction from different patients. (a) Input intraoral image. (b) Ground truth segmentation interest marked by expert. (c) Prediction results, with red, yellow and green refer to diseased, questionable diseased and healthy respectively. (Reproduced from [1])
Project Summary
Background: Gum disease is one of the most prevalent plaque initiated dental diseases. Although most patients brush their teeth every day, they cannot keep all their teeth clean. Areas in the mouth that are difficult to access, such as crowded areas, posterior teeth or interdental areas, are usually affected. After a thorough professional tooth cleaning, dental plaque will begin to accumulate on the tooth surface near the gum edge within a few days. Clinical studies indicating that regular disruption to the plaque is needed so can prevent and arrest gum disease. However, dental diseases may take years to develop, patients usually do not have any pain and symptoms unless the disease have progressed to the advanced stage. Significant resources have been used to motivate patients to keep their mouth clean but the results are not satisfactory. Automated technique is therefore desirable for monitoring oral health daily so the patients can seek for treatment when it is needed. Key issues: Patients’ response to plaque accumulated at the gum margin is by inflammation which brings more blood cells to the site to fight against the bacterial invasion. Inflammation of gum is manifested as an increase in redness (color), an increase in volume (oedema), and loss of surface texture characteristics. These affected areas can be identified by visual inspection with the dentist during the consultation or using intraoral photography. This requires professional dental training but the results often show significant variability among dentists which means low repeatability. Objectives: The objective of this research is to apply deep neural network technology to detect gum inflammation and its continuous monitoring accurately from intraoral photos. Problem: From preliminary study with 447 standard intraoral photographs, of which 337 image samples were used for training and 110 images for validation, it is found that the decoder-encoder based deep neural network approaches can fairly identify the inflammation area. However, the predicted results were not consistent under small image transformations such as shifting, scaling and rotation. It is not of sufficient quality to enable inflammation status monitoring over time. Plan: We plan to have an extensive study of deep neural architecture to deliver automatic inflammation detection with high sensitivity and specificity. and we will further collect 1200 cases of standardized intraoral photography for better neural network training. Fig 1. Selected prediction results on the validation dataset using the proposed AI system. Rows (I)-(VI) show the input images and prediction from different patients. (a) Input intraoral image. (b) Ground truth segmentation interest marked by expert. (c) Prediction results, with red, yellow and green refer to diseased, questionable diseased and healthy respectively. [1] G.-H. Li, T.-C. Hsung, B. W.-K. Ling, W. Y.-H. Lam, G. Pelekos, and C. McGrath, “Automatic Site-Specific multiple level gum disease detection based on deep neural network,” in 2021 15th International Symposium on Medical Information and Communication Technology (ISMICT2021), Xiamen, China, Apr. 2021.


